Cloud Infrastructure Management: Best Practices, Tools, Benefits & Challenges for Businesses
Sponsored Ads
Managing cloud infrastructure has become one of my top priorities as businesses increasingly move their operations online. With so many services and applications relying on the cloud, I understand the importance of keeping everything running smoothly and securely. The right approach can make all the difference between seamless performance and frustrating downtime.
I’ve seen firsthand how effective cloud infrastructure management can boost productivity and cut costs. It’s not just about keeping servers up; it’s about having the flexibility to scale, the tools to monitor resources, and the strategies to stay ahead of potential issues. As I dive deeper into this topic, I’ll share what I’ve learned about making cloud management work for any organization.
Overview of Cloud Infrastructure Management
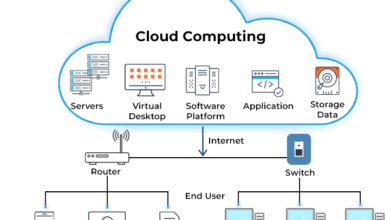
Cloud infrastructure management is the ongoing process of controlling and optimizing computing resources that live on the cloud. These resources include servers, storage, networking tools, databases, and software platforms. Managing this infrastructure requires a combination of technical skills and strategy to align with both operational needs and business objectives.
A key part of cloud management is centralization. With the right platform, I can track resource usage and system performance through a single dashboard. This helps prevent resource sprawl—a common challenge in which unused or lightly used resources accumulate and inflate costs. Automated tools alert me to unusual patterns or potential issues, allowing me to take action before small problems escalate.
Another essential component is scalability. Cloud environments enable me to scale up or down rapidly in response to demand. For example, if an e-commerce site sees a spike in users during a sale, I have the option to allocate more server space or bandwidth quickly. Automation features make this process seamless, saving time and reducing the risk of outages.
Security is always top of mind when managing the cloud. I regularly monitor access controls, encryption settings, and compliance requirements to ensure adherence to these standards. Centralized management enables me to enforce policies consistently across all resources. Plus, most major cloud providers offer built-in security dashboards to help flag vulnerabilities before they become threats.
Cost management is another major factor. With detailed reporting features, I can track usage for each resource and optimize spending. Some platforms allow me to set budget alerts or automate resource scaling to fit my budget in real-time.
Cloud infrastructure management also includes regular updates, patch management, and backup procedures. I schedule these tasks to minimize downtime and ensure my infrastructure runs smoothly and securely. This proactive approach helps maintain business continuity and protects critical data.
The tools and platforms available today range from basic dashboards to full-featured suites, such as AWS Management Console, Microsoft Azure Portal, and Google Cloud Console. The right choice depends on the business’s size, complexity, and specific industry needs.
Key Features of Cloud Infrastructure Management

Cloud infrastructure management solutions provide a comprehensive set of features designed to streamline system operations and optimize efficiency. Each feature plays a distinct role in maintaining optimized and secure business workloads.
Automation and Orchestration
Automation is a standout feature for me because it significantly reduces the need for manual intervention. Routine tasks, such as server provisioning, patch management, and scaling, can be set up to run automatically. Orchestration takes it a step further by coordinating these automated tasks across different resources and environments. I have found this especially effective during disaster recovery drills and large-scale deployments, where consistency is crucial. By automating repetitive processes, I see fewer human errors and enjoy faster responses to business demands.
Monitoring and Reporting
Accurate monitoring is the backbone of reliable cloud management. Dashboards display real-time metrics on resource usage, performance, uptime, and potential bottlenecks. I rely on comprehensive reporting tools to receive detailed analytics and historical trends, which help me quickly identify inefficiencies or unexpected spikes. Most platforms offer customizable alerts, enabling me to address issues before they disrupt critical services.
Security and Compliance
Security tools are integrated into most cloud management platforms, covering encryption, identity management, and audit logging. Access control policies make sure only authorized users can interact with sensitive data or configurations. Compliance checks run automatically, flagging resources that do not meet required industry standards such as GDPR or HIPAA. I find these features critical for maintaining trust, especially when managing data across different regions.
Scalability and Flexibility
A main appeal of cloud infrastructure management is its inherent scalability. When seasonal spikes or sudden surges occur, resources adjust on demand without service interruptions. With auto-scaling configurations, I can efficiently allocate resources based on real-time workload needs, minimizing both latency and unnecessary expenses. Flexibility extends to supporting hybrid and multi-cloud environments, letting me tailor infrastructure setups to changing business priorities.
Integration Capabilities
Integration ensures cloud systems can connect with existing business tools and third-party services. Most platforms support APIs, plugins, or connectors for a wide range of applications, including CRM software, monitoring tools, and DevOps pipelines. By leveraging pre-built integrations, I reduce setup times and create seamless workflows. This compatibility is invaluable when migrating legacy systems or building new solutions that require interaction with diverse environments.
Pros of Cloud Infrastructure Management
Cloud infrastructure management offers several key advantages that enable organizations to operate more effectively in the digital landscape. I have seen firsthand how well-implemented management practices can transform productivity and resource control in a business environment.
Improved Operational Efficiency
With cloud infrastructure management tools, I can automate repetitive tasks like server provisioning, backup scheduling, and patch deployment. This level of automation not only reduces manual errors but also frees up my team’s time to focus on higher-value activities. Centralized dashboards enable me to monitor the entire environment in real-time, allowing me to identify and resolve potential issues before they impact performance quickly. The orchestration of workflows across multiple services ensures consistency and speed, especially when rolling out updates or recovering from unexpected outages.
Enhanced Security Measures
Security is always top of mind, and with built-in management features, I can enforce security policies across all cloud resources. These platforms make it simple to set roles and permissions or monitor access logs. Proactive security monitoring tools alert me to threats the moment they emerge, allowing me to respond before any damage occurs. I appreciate the compliance modules that help me maintain regulatory standards without manual oversight. Regular automated updates and patches ensure that systems stay protected against new vulnerabilities.
Cost Optimization
One of the standout benefits I experience is detailed financial reporting and budget controls. Real-time analytics help me track resource usage and identify areas where I am overspending or underutilizing assets. With budget alerts and cost forecasting, I can align spending with organizational priorities and avoid surprising overages at the end of the month. This precise control lets me scale resources up or down to match demand, ensuring I only pay for what I use.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Operational Efficiency | Automation, centralized monitoring, reduced manual work, consistent workflow orchestration |
| Enhanced Security | Policy enforcement, real-time threat alerts, automated compliance, regular patch management |
| Cost Optimization | Real-time analytics, budget alerts, cost forecasting, pay-per-use resource scaling |
Cons of Cloud Infrastructure Management
While cloud infrastructure management offers impressive benefits, it also has some limitations that I have encountered. These challenges can affect resource planning, project timelines, and overall business strategies if not carefully addressed.
Complexity of Implementation
Managing cloud environments can be challenging. Setting up cloud infrastructure often means working with multiple vendors, complex networking, and a range of integration points. I have found that the initial configuration can overwhelm even experienced IT teams, especially when shifting from on-premises systems. Adopting automation, orchestration, and monitoring tools may require extensive training, and misconfigured resources can lead to performance bottlenecks or unexpected downtime.
Potential Security Risks
Although cloud platforms invest in strong security, the shared responsibility model means I am still accountable for many aspects of data protection. Misconfigured permissions, unsecured application programming interfaces (APIs), or inconsistent policy enforcement can expose sensitive information. Rapid provisioning and scaling introduce more endpoints to monitor, increasing the attack surface. Keeping up with constantly evolving threats and compliance regulations adds another layer of complexity to my security management workload.
Ongoing Maintenance Requirements
Cloud infrastructure is not a set-it-and-forget-it solution. Regular maintenance is crucial to avoid disruptions and inefficiencies. I need to oversee system updates, patch vulnerabilities, monitor resource usage, and review access controls to prevent drift from secure and optimal configurations. These tasks are continuous and often demand dedicated roles or teams. Without ongoing attention, I risk failing audits, overspending, or suffering from degraded system performance.
Performance and User Experience
Cloud infrastructure management platforms shape daily workflows for IT teams and end users. In my experience, these tools can make or break the success of a cloud environment based on how intuitive, reliable, and adaptable they are to business needs.
Ease of Use and Accessibility
A robust cloud infrastructure management solution should provide an interface that strikes a balance between power and simplicity. I have found that dashboards with point-and-click controls and guided setup wizards help reduce the learning curve for newcomers. Multi-language support, browser-based access, and mobile compatibility are also increasingly important. When I can manage resources from anywhere using a secure portal or mobile app, it streamlines daily monitoring and on-the-go troubleshooting. However, advanced features behind nested menus or technical jargon can slow down less experienced users, so platforms that prioritize accessibility usually win me over. Integration with single sign-on services adds both convenience and reduced friction for enterprises with large teams.
Reliability and Uptime
Consistent performance is a dealbreaker. Most cloud management platforms offer 99.9% uptime or higher, featuring built-in redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure continuous operation. In practice, these reliability safeguards protect my systems from unplanned outages and maintain stable service delivery. Scheduled maintenance notifications and automated backup solutions provide additional peace of mind. Below is a comparison of typical uptime guarantees from major providers.
| Provider | Uptime Guarantee | Multi-Region Support | Automated Backups |
|---|---|---|---|
| AWS Management Console | 99.99% | Yes | Yes |
| Azure Portal | 99.95% | Yes | Yes |
| Google Cloud Console | 99.95% | Yes | Yes |
Despite these assurances, actual reliability may still depend on the underlying internet connection, third-party integrations, and custom workload requirements. I always recommend reading the fine print of service-level agreements to understand potential downtime allowances and compensation clauses truly.
Customization Options
One of the standout strengths of cloud infrastructure management is its flexibility. I appreciate it when platforms allow for role-based permissions, automated workflow scripts, and personalized dashboards. Through APIs and plugin ecosystems, I can create custom alert triggers or resource templates that fit my team’s exact processes. White-labeling options and widget-based analytics further tailor the experience to brand or departmental standards. That said, some tools offer limited customization unless you invest in premium tiers or additional modules, so it is essential to assess your actual needs against the product’s scalability. The ability to grow and adapt the management interface is often a key reason I stick with one provider over another.
Comparison With Alternatives
Cloud infrastructure management has transformed IT operations; however, it is essential to compare it with other approaches and solutions. I find that the choice often depends on business goals, technical resources, and the need for agility.
Traditional Infrastructure Management
Traditional infrastructure management relies on physical hardware stored on-premises. In my experience, this approach demands a dedicated IT team for hands-on support and maintenance. Scaling up requires purchasing and installing new servers, which can result in downtime and higher upfront costs. Resource allocation often becomes inefficient with underused hardware sitting idle during quiet periods. Although direct control over security can be a benefit, updates and patches must be handled manually, which increases the risk of vulnerabilities. Compared to traditional cloud management methods, businesses now expect flexibility and speed.
Leading Cloud Management Platforms
Several cloud management platforms dominate the market, each offering unique strengths. I have worked with tools such as the AWS Management Console, Microsoft Azure Portal, and Google Cloud Console. These platforms provide centralized dashboards, automation tools, and real-time monitoring capabilities. Their scalability far surpasses that of traditional systems, allowing companies to spin resources up or down in minutes.
Here is a quick comparison of their core features:
| Platform | Centralized Dashboard | Automation | Monitoring & Reporting | Scalability | Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS Management | Yes | Robust | Detailed | Instant | Extensive |
| Azure Portal | Yes | Advanced | Comprehensive | Instant | Wide Microsoft |
| Google Cloud | Yes | Strong | Customizable | Instant | Google ecosystem |
While most leading platforms offer user-friendly interfaces, advanced security controls, and extensive integration options, some tools limit certain features to higher pricing tiers. Overall, modern cloud management platforms streamline resource control in ways traditional infrastructure cannot.
Open Source vs. Proprietary Solutions
Choosing between open source and proprietary cloud management tools is a strategic decision. Open source solutions like OpenStack and CloudStack can be a good fit for teams with strong technical expertise. They offer enhanced customization and control, and licensing fees are often minimal. However, I have observed that open-source options typically require more initial configuration and ongoing support from skilled staff.
Proprietary platforms, such as VMware vRealize and Cisco CloudCenter, tend to offer polished user experiences, professional support, and official security updates. These tools often include automation, reporting, and integration out of the box, which reduces the learning curve. On the downside, they come with licensing costs and may restrict customizations through vendor lock-in.
Weighing these alternatives against standard cloud infrastructure management, open-source tools are well-suited for organizations with highly specific needs and internal expertise. At the same time, proprietary solutions deliver reliability and ease of use for most businesses. The best fit depends on budget, team skills, and long-term flexibility requirements.
Hands-on Experience and Real-world Testing
Getting practical with cloud infrastructure management tools reveals what the documentation and marketing often overlook. My trials with leading platforms uncovered both user-friendly strengths and some hidden hassle points in the everyday workflow.
Initial Setup and Configuration
During the initial setup, I noticed a significant difference in the onboarding experience. Platforms like AWS and Azure guided me with step-by-step wizards for account creation, resource group setup, and basic security configuration. Setup times varied based on the complexity of my project. For a standard virtual server deployment, I had a working environment up and running in under 20 minutes on most major platforms. Configuring network firewalls and permissions took longer, especially on systems with granular access controls. The option to automate setup using templates or scripts was helpful, as it reduced the room for human error and made repeatable deployments straightforward. When using open-source solutions, I needed to invest extra time learning their terminology and dependencies before I could get started.
Managing Workloads and Resources
Day-to-day management stood out as the area where usability made or broke the experience. Manipulating workloads through a centralized dashboard felt intuitive on proprietary platforms. I could spin up virtual machines, adjust storage allocations, and monitor system health without having to hunt through complicated menus. Auto-scaling rules and scheduled jobs worked reliably, ensuring resources would spike during heavy loads and scale back afterward to save costs. However, on open-source tools, although deeper customization was possible, the learning curve grew steep. Managing hybrid or multi-cloud setups highlighted the importance of aggregation features, as lacking them resulted in fragmented monitoring and increased manual tracking. I also noticed that integrated alerting systems promptly flagged anomalies, helping me resolve CPU bottlenecks or failing storage nodes before they impacted end-users.
Support and Documentation
My evaluation of support and documentation exposed clear differences between platforms. Commercial offerings, such as Azure and Google Cloud, provided searchable knowledge bases, helpful video tutorials, and responsive ticket-based support channels. In several instances, I resolved deployment issues by following step-by-step guides within minutes. The dedicated community forums for open-source solutions offered a valuable resource for troubleshooting, but answers sometimes took longer to surface and often assumed familiarity with complex technical language. API documentation quality varied, with some platforms offering well-organized reference materials and others making me sift through outdated or scattered pages. Overall, prompt and thorough documentation had a direct impact on reducing downtime during both setup and daily management.
Conclusion
Cloud infrastructure management continues to evolve, and so do the demands on IT teams. I’ve found that staying flexible and prioritizing ease of use can make all the difference when choosing a management platform. The right mix of automation, security, and visibility not only streamlines operations but also empowers teams to focus on bigger goals. As cloud technology advances, I’ll continue to explore new strategies and tools to help businesses maximize the value of their infrastructure investments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cloud infrastructure management?
Cloud infrastructure management is the process of controlling, optimizing, and securing cloud-based computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, using centralized tools to maximize efficiency, maintain uptime, and ensure cost-effectiveness.
Why is cloud infrastructure management important for businesses?
Effective cloud management ensures smooth operations, enhanced security, scalable resources, and effective cost control. It helps businesses maintain productivity, prevent resource waste, and quickly adapt to changes in demand.
How does cloud management improve security?
Cloud management platforms provide security features such as access controls, regular monitoring, and compliance enforcement. These tools help protect sensitive data, detect threats early, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
What are the key benefits of cloud infrastructure management?
The main benefits include improved operational efficiency, better security, automated tasks, real-time monitoring, and cost optimization through budgeting and resource tracking.
What challenges come with cloud infrastructure management?
Common challenges include complex implementation, managing multiple vendors, ongoing maintenance, potential security risks, and the need for specialized IT skills.
How do automation and orchestration help in cloud management?
Automation and orchestration reduce manual tasks, ensure consistency, speed up server provisioning, streamline workflows, and support disaster recovery, making cloud management more efficient.
What makes centralized dashboards valuable in cloud management?
Centralized dashboards provide a unified view for monitoring resource usage, system performance, and security across all cloud assets, enabling teams to identify and resolve issues quickly.
How do cloud management platforms support scalability?
These platforms enable organizations to scale resources up or down rapidly in response to demand, particularly during peak usage periods, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
What’s the difference between cloud and traditional infrastructure management?
Traditional management relies on physical hardware and requires more manual intervention, whereas cloud management utilizes automated, scalable resources that can be accessed remotely, resulting in greater flexibility and lower costs.
How do open-source and proprietary cloud management tools compare?
Open-source tools offer flexibility and customization for experienced teams, while proprietary solutions provide easier setup, user-friendly interfaces, and professional support, often at a higher cost.
What should organizations consider when choosing a cloud management platform?
Key considerations include budget, required features, team skills, security needs, integration capabilities, and the ability to scale or customize as the business grows.